Posted in : Artificial Intelligence I
Artificial Intelligence 1 - Agents
Agents and Environments
An agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving its environment throgh sensors and acting upon that environment through actuators.

Rational Agents
We can use a fixed performance measure to evaluate the environment sequence. This measure usually reward the agent when it does actions that have good effects on the environment and penalize it otherwise.
A rational agent chooses whichever action maximizes the expected value of the performance measure given the percept sequence to date.
Functions and Agent Programs
The agent function maps from percept histories to actions:
In an idealistic implementation we can have a table that lists all the possible percept histories of the agent with the associated action to execute. This approach is unfeasable because of the huge size of the resulting table.
A more pratical implementation is the use of a program that keep track of the sequence of percepts and choose the best action for each new percept.
The agent program runs on the physical architecture to produce .
PEAS
To design a rational agent, we must specify the task environment:
- Performance Measure
- Environment
- Actuators
- Sensors
Environment’s Features
The agent environment can be: * Totally or partially observable * Deterministic, non-deterministic, stochastic or strategic * Episodic or sequential * Static, dynamic or semidynamic * Discrete or continuos * Single-angent or multi-agent
The environment influences the agent design.
Agent types
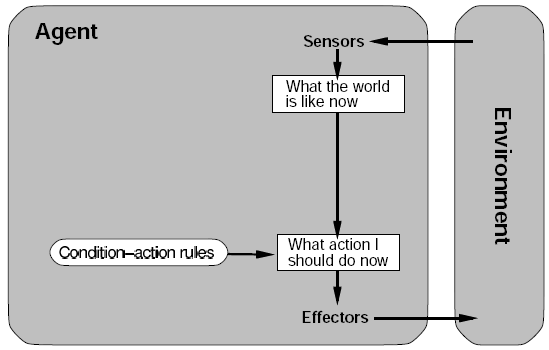
- Simple reflex agent
-
Reflex agent with state
-
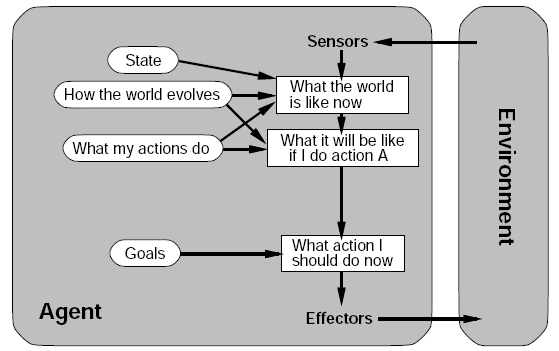
Goal-based agent
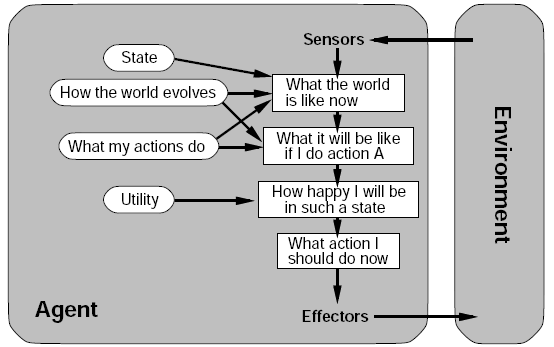
- Utility-based agent
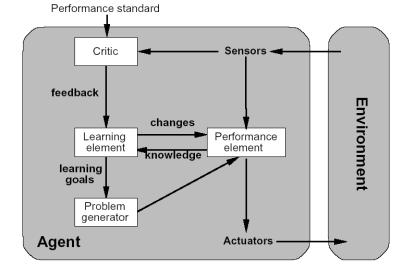
- Learning agent